
It was suspected that the heat treater carbonitrided the parts, resulting in a brittle structure. To verify this assumption, Paulo also carbonitrided samples, which exhibited similar brittle characteristics.
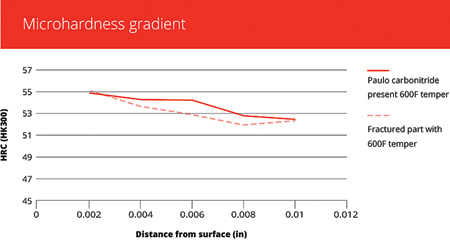
Both the Paulo carbonitrided part and the customer's part exhibited similar microhardness behavior after being tempered at 600 °F. This helps confirm the problem description.
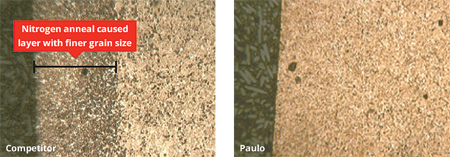
The micrograph on the left shows that the standard 1045 does not have sufficient hardenability to overcome the fine grain produced during the annealing process. The micrograph on the right shows how the chromium spike was sufficient for overcoming this fine grained surface condition.
A Chicago-area automotive part supplier encountered frequent cracking of variable valve timing plates that were sent to a third party for heat treatment. The problem resulted in the company spending a lot of time and money on part testing as well as wasting a lot of steel. After a thorough examination of the manufacture and heat treatment of the parts, Paulo metallurgists identified the cause of the cracking and recommended a custom solution to keep it from happening in the future.
Part Failure Investigation
Being an integral part of customers' success means more than just regularly receiving parts and treating them according to spec.
Sometimes a customer approaches a heat treater in search of answers to a problem they cannot quite grasp.
In this case, a Chicago-area supplier of automotive components needed to know why parts it sent off for heat treating kept coming back cracked. They were spending too much time and resources on tests and throwing out too many failed parts.
Persistent Cracks in Variable Timing Plates
Our customer produces variable valve timing (VVT) plates for domestic automobile models. VVT plates are part of a system designed to optimize engine performance by changing the lift, duration and timing of valve lift events.
In this case, the life cycle of these parts began in a steel mill, where coils of AISI 1045 carbon steel were produced. The parts were then annealed in preparation for fine blanking at our customer's facility. Then, the parts would be through-hardened and sent to the automotive manufacturer.
But our customer noticed that many of the parts came back cracked. This was the source of two big problems:
- The customer had to perform inspections on every part that was returned from the heat treater, which came at significant expense of time and resources.
- To satisfy the terms of its contract with the automotive manufacturer, our customer had to make far more parts than it would have ordinarily needed to on the assumption that many of the parts would not be acceptable. It cost too much money, and too much steel was wasted.
The customer approached metallurgists at Paulo to figure out what was wrong and what could be done to make it right.
Forensic Heat Treatment Analysis
Our first task was to figure out what the customer's heat treater was doing to the parts.
Upon our inspection, we noticed the parts were quite brittle. A closer look at the microstructure of the parts' surfaces revealed they had been carbonitrided.
Meanwhile, we consulted with personnel at the mill and steel processor where the steel originated. We learned that the coils of 1045 steel were annealed in a nitrogen environment. Annealing is an important process that spheroidizes carbides in the steel, which aids in fine blanking. In the case of our customer, the VVT plates could not be formed to the specified tolerance if they were not first annealed.
But the nitrogen present in the anneal was a problem. 1045 steel includes aluminum as a grain refining element. When aluminum and nitrogen combine during annealing, aluminum nitrides form. Aluminum nitrides create a much finer grain on the part surface, which prevents the full hardening of the material. We suspected our customer's heat treater attempted to overcome the defect by carbonitriding. But instead of hardening, the parts just got brittle. That is because 1045 steel lacks the hardenability that would be required to overcome the fine grain size that resulted from the presence of aluminum nitrides.
To confirm our suspicion, we ordered the same material from the customer's mill and then carbonitrided the parts as we believed the previous heat treater had. Our post-treatment analysis of the parts shows the successful recreation of the failure mode.
A Custom-Developed Solution
We believed the most direct way to solve the problem was to eliminate the factors that caused it at the start. We again approached the mill, this time to see if they could anneal the steel in a different environment. They said they could not.
The next best thing would be to "spike" the 1045 steel with another alloying element that would add hardenability despite the fine grain sizes that result when nitrogen and aluminum interact during annealing. We pinpointed chromium as the ideal alloy, and after some trial and error we identified a formula for the chromium spike that would result in fully-hardened parts without cracks after through hardening.
Today, the customer's mill still produces the 1045 steel with our recommended chromium spike. And as of mid-2018, we have treated 25 million variable valve timing plates for this customer.
This case study illustrates the importance of a few key lessons suppliers should keep in mind. First, stay in touch with what is going on further up the supply chain. You may be able to react to problems more quickly, or stop them altogether.
Second, have a working knowledge of part materials and the chemistry at play during any manufacturing process. Armed with this knowledge, you can ask key questions as you vet potential heat treatment partners. It could end up saving you time and expense in the long run.
Finally, know where to get a second opinion, and have a backup heat treater ready in case your primary partner cannot do what you need them to do.
About Paolo
Founded in 1943, Paulo is one of the largest providers of heat treating, brazing and metal finishing solutions in North America. Headquartered in St. Louis, Paulo operates six divisions servicing the Midwest, Great Lakes and Southeast regions of the U.S. as well as northern Mexico.
Authored by Rob Simons, Metallurgical Engineer, Paulo
For more information contact:
Paulo
5711 West Park Ave
St. Louis, MO 63110
314-647-7500
www.paulo.com